Caesar Cipher
In cryptography, a Caesar cipher is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a right shift of 3, A would be replaced by D, B would become E, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence
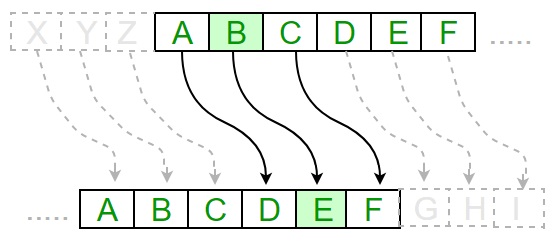
The following python program shows how the Caesar cipher works.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
def encrypt(text,s):
result = ""
# transverse the plain text
for i in range(len(text)):
char = text[i]
if (char.isupper()):
result += chr((ord(char) + s - 65) % 26 + 65)
else:
result += chr((ord(char) + s - 97) % 26 + 97)
return result
text = "I am an awesome cskitty"
s = 4
print "Plain Text : ", text
print "Shift pattern : ",str(s)
print "Cipher: " + encrypt(text,s)
Question: can you design a decryption function?