Dijkstra’s Shortest Path
Explanation
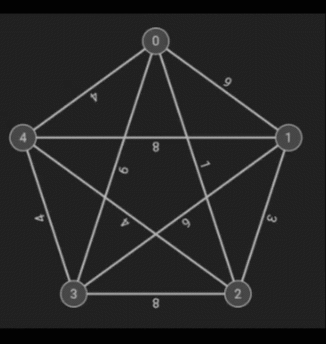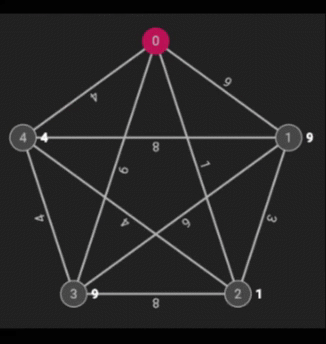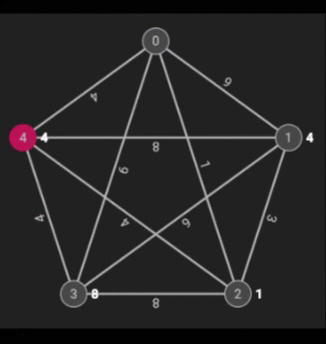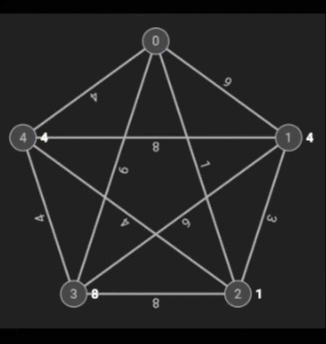
Dijkstra’s Shortest Path is an algorithm that finds the shortest (as in the best) path that involves the least amount of weight. The weight of a node is determined by the minimum weight on any path from the starting node (in this case, 2).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int node;
int distance;
public Node(int n, int w) {
node = n;
distance = w;
}
}
class NodeComparator implements Comparator<Node>{
public int compare(Node s1, Node s2) {
if (s1.distance > s2.distance) {
return 1;
}
else if (s1.distance < s2.distance) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
}
public class DijkstraShortestPathA {
Set<Integer> m_visited;
PriorityQueue<Node> m_myQueue;
int m_size;
int[] m_distances;
public int[][] m_graph;
public DijkstraShortestPathA(int N) {
m_visited = new HashSet<Integer>();
m_myQueue = new PriorityQueue<Node>(N, new NodeComparator());
m_distances = new int[N];
m_size = N;
m_graph = new int[N][N];
}
int[] path_finder(Node startingNode) {
// step 0: initialize distance array from starting node
for (int i = 0; i < m_size; i++) {
m_distances[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
m_distances[startingNode.node] = 0;
// step 1: push starting node into queue
m_myQueue.add(startingNode);
// step 2: while loop
while(m_myQueue.size() > 0) {
Node n = m_myQueue.poll();
m_visited.add(n.node);
// step 3: process neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < m_graph[n.node].length; i++) {
// step 4: process and insert neighbor node into priority queue
if (m_graph[n.node][i] != 0 && n.node != i){
// calculate new distance = distance(n) + edge(n, i)
int currentDistance = m_graph[n.node][i] + n.distance;
if (currentDistance < m_distances[i]) {
m_distances[i] = currentDistance;
}
if (! m_visited.contains(i)) {
m_myQueue.add(new Node(i, m_distances[i]));
}
}
}
}
return m_distances;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
DijkstraShortestPathA dsp = new DijkstraShortestPathA(5);
dsp.m_graph[0][1] = dsp.m_graph[1][0] = 1;
dsp.m_graph[0][2] = dsp.m_graph[2][0] = 8;
dsp.m_graph[0][3] = dsp.m_graph[3][0] = 6;
dsp.m_graph[0][4] = dsp.m_graph[4][0] = 7;
dsp.m_graph[1][2] = dsp.m_graph[2][1] = 7;
dsp.m_graph[1][3] = dsp.m_graph[3][1] = 4;
dsp.m_graph[1][4] = dsp.m_graph[4][1] = 9;
dsp.m_graph[2][3] = dsp.m_graph[3][2] = 1;
dsp.m_graph[2][4] = dsp.m_graph[4][2] = 6;
dsp.m_graph[3][4] = dsp.m_graph[4][3] = 6;
int[] returnlst = dsp.path_finder(new Node(2, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < returnlst.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d, ", returnlst[i]);
}
}
}