Flood Fill
Explanation
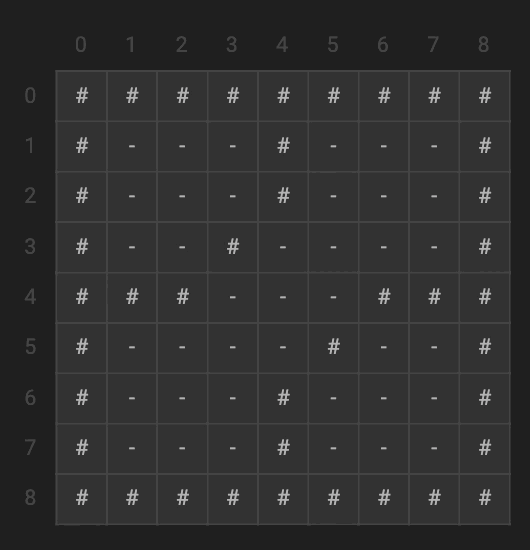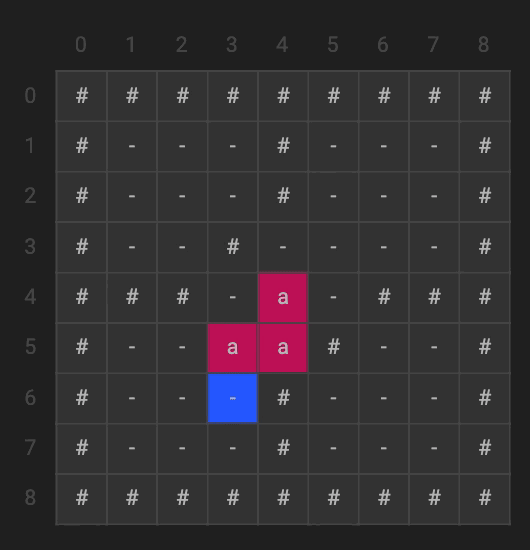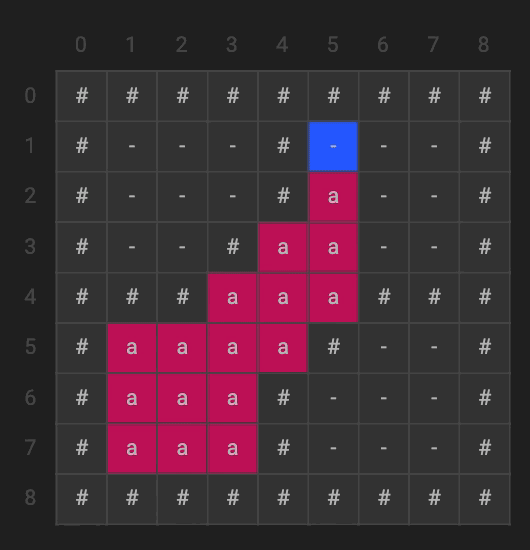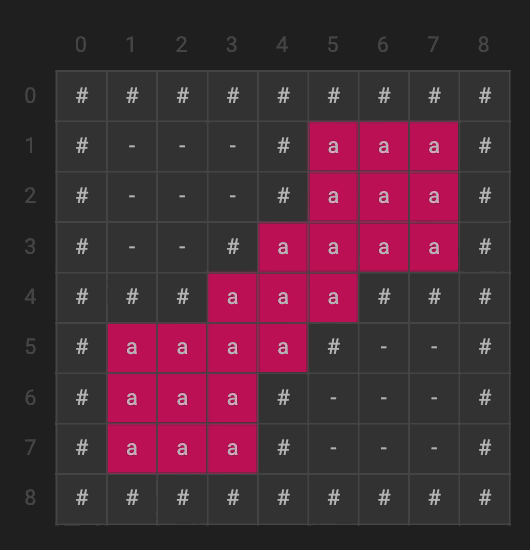
The flood fill algorithm uses a recursive method to try and fill all of the empty (denoted by the ‘-‘) spaces on the 2D matrix. The boundary case is when it hits or goes past one of the walls; namely, when x or y is less than 0 or greater than the length of the matrix. We can see that we start at any empty node, then begin recursing through all of its neighbors until all of the possible neighbors are filled or a wall.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public class FloodFill {
char G[][] = {
{'#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '#', '#', '-', '-', '-', '#', '#', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '-', '-', '-', '#', '-', '-', '-', '#'},
{'#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#', '#'},
};
void printG() {
for (int i = 0; i < G.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G[0].length; j++) {
System.out.printf(G[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
void flood(int x, int y, char newColor) {
if (x < 0 || x > G.length - 1 || y < 0 || y > G[0].length - 1) {
return;
}
else {
if (G[x][y] == '-') {
G[x][y] = newColor;
// checking neighbors
flood(x + 1, y, newColor);
flood(x - 1, y, newColor);
flood(x, y + 1, newColor);
flood(x, y - 1, newColor);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
FloodFill floodFill = new FloodFill();
System.out.println("Before:");
floodFill.printG();
floodFill.flood(4, 4, 'a');
System.out.println("After:");
floodFill.printG();
}
}