Hamiltonean Cycles
Explanation
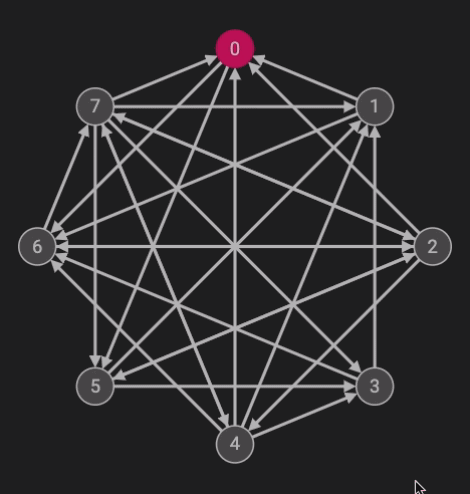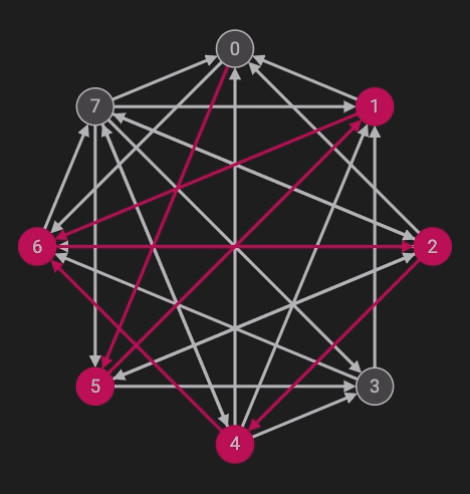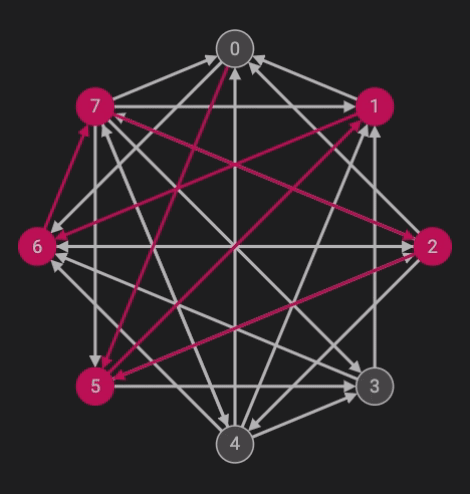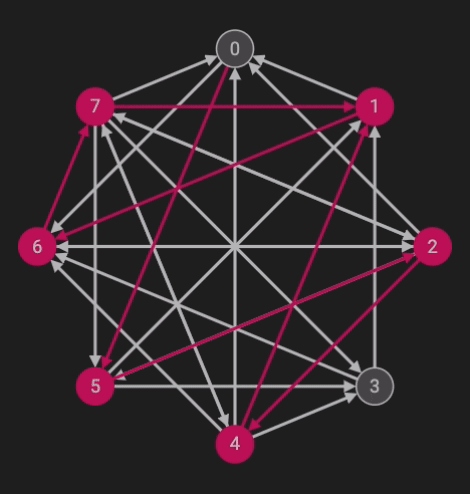
The Hamiltonean Cycles algorithm is an implementation of backtracking. The problem calls for finding a cycle starting with one node (in this case, node 0) which traverses through all of the nodes once. Below is the code written in java.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class HamiltonianCycle {
List<List<Integer>> currentlst = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> makeDeepCopyInteger(List<Integer> old){
ArrayList<Integer> copy = new ArrayList<Integer>(old.size());
for(Integer i : old){
copy.add(new Integer(i));
}
return copy;
}
List cyclefind(int currentNode, List<Integer> path, int[][] graph) {
// base case
List<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<Integer>(Collections.nCopies(graph.length, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
if (nodes.get(path.get(i)) != 0) {
List<Integer> returnlst = new ArrayList<Integer>();
return returnlst;
} else {
nodes.set(path.get(i), 1);
}
}
if (! nodes.contains(0)) {
return path;
}
else {
boolean returnval = false;
List<List<Integer>> possibilties = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < graph[0].length; i++) {
if (path.size() < 4 && i == 0) {
continue;
}
else if (graph[currentNode][i] == 1) {
path.add(i);
List<Integer> value = cyclefind(i, path, graph);
if (path.size() == nodes.size() && (value.size() > 0) && (path.get(path.size() - 1) == 0)) {
currentlst.add(makeDeepCopyInteger(path));
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
return currentlst;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
HamiltonianCycle hamiltonianCycle = new HamiltonianCycle();
int[][] mygraph = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> x = hamiltonianCycle.cyclefind(0, path, mygraph);
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) {
System.out.print("0 ");
for (int j = 0; j < x.get(i).size(); j++) {
System.out.print(x.get(i).get(j));
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}